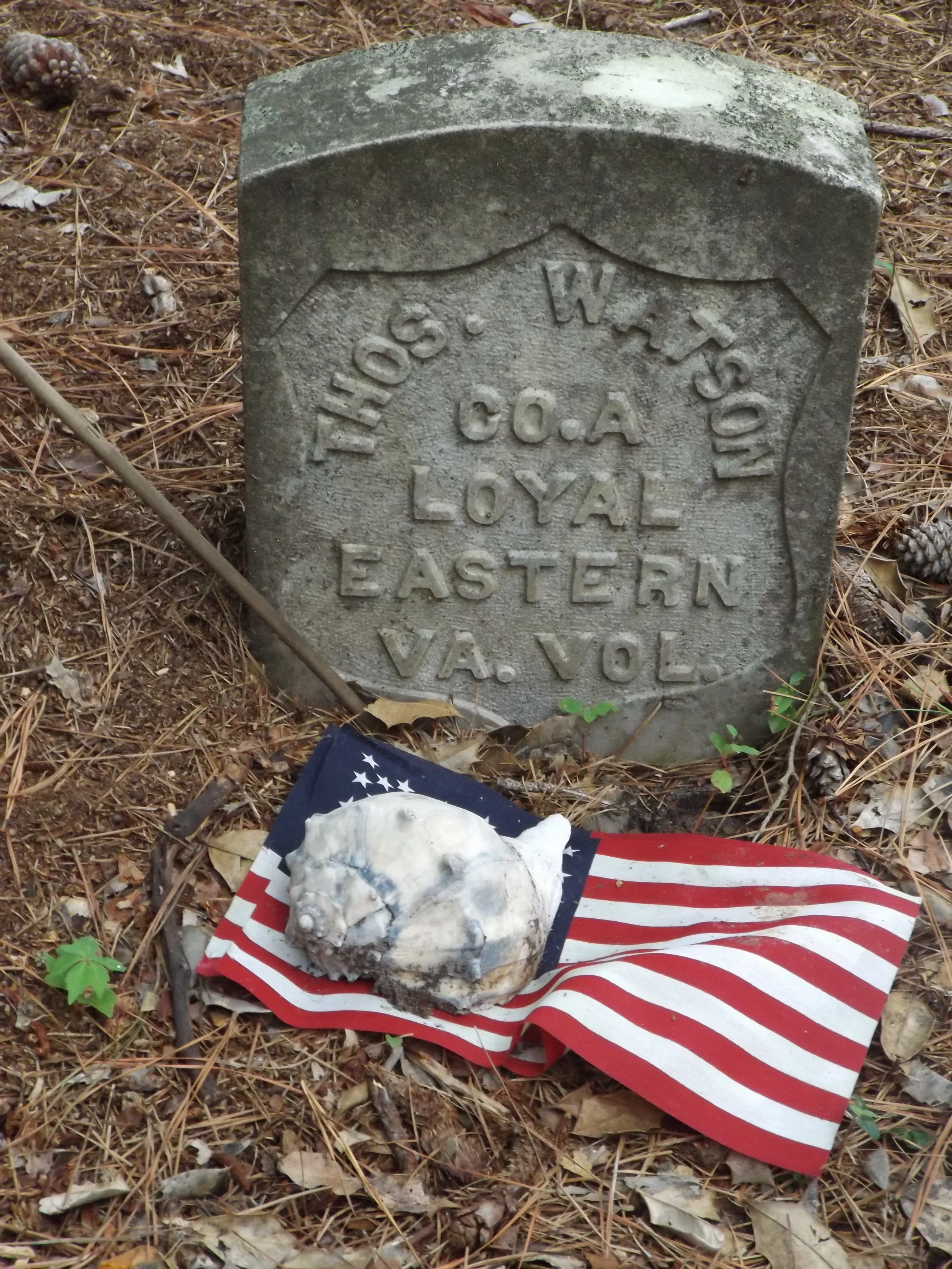
Scapegoat or Scandal? J.E.B. Stuart and the Battle of Gettysburg
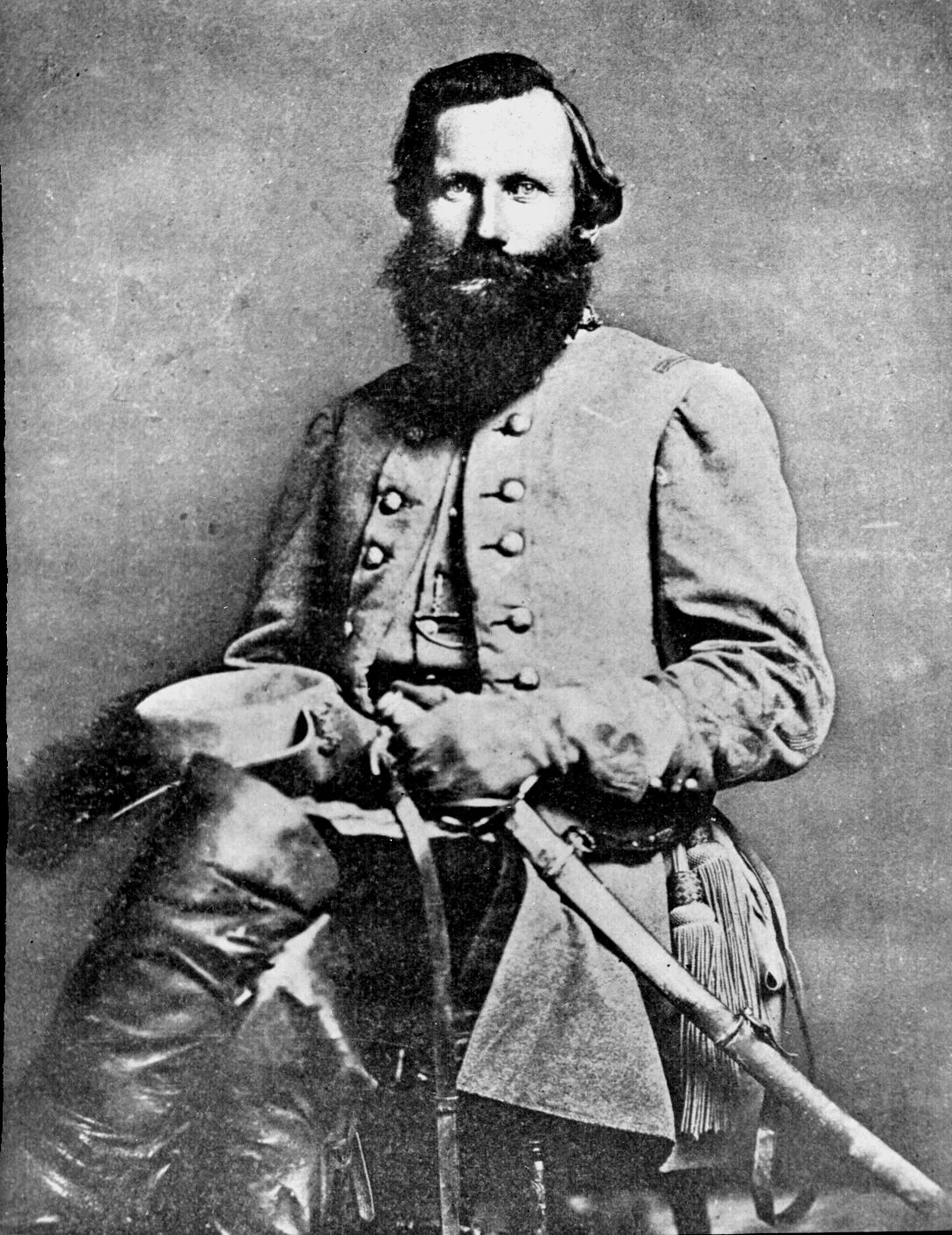
/The June 12th, 1863 edition of the Richmond Examiner seethed. Just days before, Confederate cavalry had been caught completely by surprise in a daring strike by their Union counterparts at Brandy Station Virginia, and only after a hard fight with the help of Southern infantry was the enemy repulsed. “But this puffed up cavalry of the Army of Northern Virginia,” the Examiner crowed, “has been twice, if not three times, surprised since the battles of December, and such repeated accidents can be regarded as nothing but the necessary consequences of negligence and bad management.” Such humiliations were unacceptable, and the Examiner concluded by charging that better organization, more discipline, and greater earnestness among “vain and weak-headed officers” was needed. Other Southern papers offered more of the same. The Richmond Sentinel called for greater “vigilance…from the Major General down to the picket.” The Charleston Mercury thought the affair an “ugly surprise,” while the Savannah Republican thought it all “very discreditable to somebody.” The commander of Confederate cavalry, James Ewell Brown (Jeb) Stuart, had to be wondering if the Brandy Station fight wasn’t “discreditable” to him...
Read More