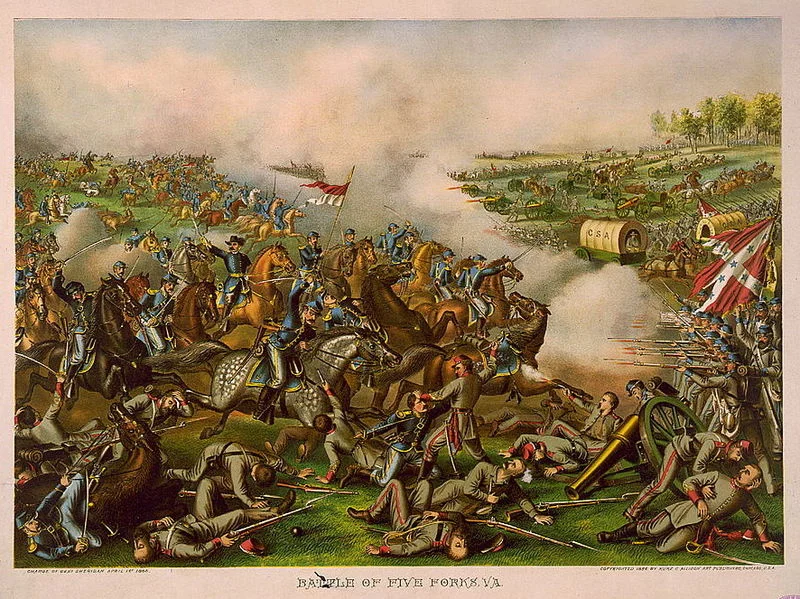
In the waning days of March 1865, as the armies in both blue and gray languished in the muddy trenches of Petersburg, Ulysses S. Grant still searched for a final, climatic battle. However, since 1861 the Civil War had transformed into a type of warfare very different than lines of soldiers advancing across open, rolling fields. As both armies settled into miles of intricately built trenches and stalemate ensued, that Clausewitzian final battle of apocalyptic proportions seemed increasingly unlikely. The end of the war would come, but in ways not even the premier military leaders of the time expected.
As winter turned to spring in 1865, Robert E. Lee’s confederate Army of Northern Virginia was suffering from a chronic lack of supplies, rising casualty figures, and heavy desertion. However, the Virginian had created an extremely strong line of defenses around Petersburg that the seemingly unstoppable juggernaut that was the Army of the Potomac had been unable to breach. Grant knew that if a weakness on this line could be found and exploited properly, it could not only mean the fall of Petersburg and subsequently Richmond, but eventually the surrender of Lee’s Army and the end of the war.
This opportunity came on Petersburg’s Western Front 150 years ago, on April 1, 1865, at a place where five roads converged. It became not only a battle of strategic importance, but also a captivating study in leadership and reputation. The Battle of Five Forks was brief, but its significance unquestionable.
Read More